Replicating Hyper-V over a WAN can be tricky when dealing with large VMs. Not only does the Internet connection at both points have to be steady, but latency, backups and other factors can break the replication process. Even if everything goes smoothly, large VMs can take weeks to replicate across a WAN connection.
To get around this, we have manual seeding. Seeding is the process of taking a VMs image, moving it to the target location, then replicating the changes that have taken place during the seeding interval. Manual seeding involved physically moving the initial image (seed) using a USB disk or other portable media. This will greatly reduce the amount of data that has to be transmitted initially.
Here we will describe the manual seeding process step by step. We will use a small USB disk (2TB) to move our initial copy from a client site (origin) to a data center (target). The requirements are that you have connectivity between the origin and destination servers and that you have Hyper-V replica already enabled on both servers.
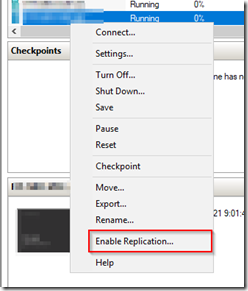
From the origin server, open the Hyper-V manager, select the VM you want to seed, right click and select enable replication.
In the specify replica server, add the name of the target server (you must already have a working WAN link over VPN). In the next dialog boxes select your connection parameters, replication VHDs, replication intervals and number of recovery points.
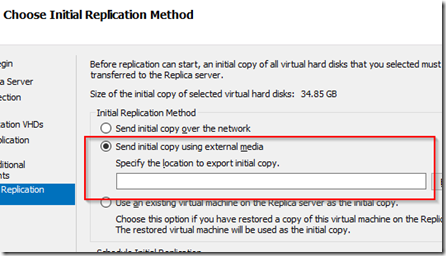
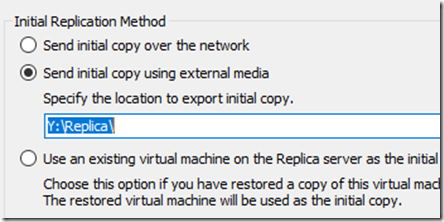
In the choose initial replication method dialog box, select the option to send initial copy using external media as shown below.
Click browse and locate the portable media (USB disk) where you want to send the initial seed copy.
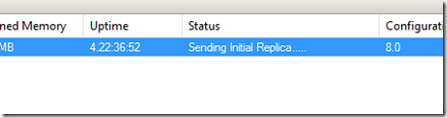
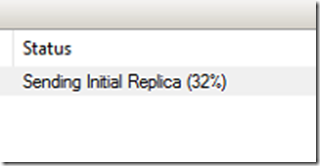
Click finish to complete and you will notice that the origin server will display a sending initial replica status.
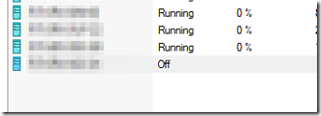
If you check the Hyper-V manager, you will notice that a VM has been created in the off state.
For now, we need to wait until the origin server completed the initial replica seed. You can see the seed progress in the status column.
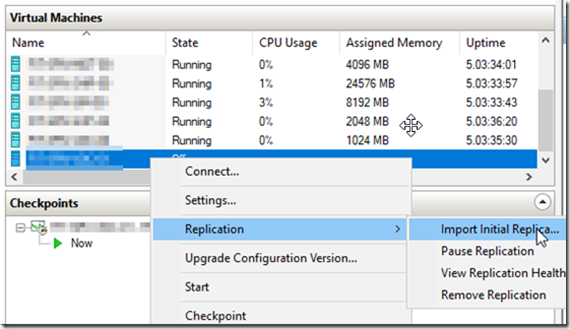
Once the initial seed replica completed, gracefully eject the USB drive. Ship the USB media to the target server’s location and connect it to the target server. From there, open the Hyper-V manager and located the newly created VM. Right click on the VM and select replication –> import initial replica as shown below.
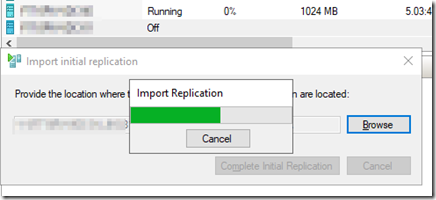
Click browse and select the folder on the USB drive where the seed image is located, then click on complete initial replication.
Wait for the import replication process to complete. Once completed, the replication will commence automatically.
Note: I have had success copying the seed image to the target location using Robocopy using the same VPN link where the Hyper-V replica failed. If your image is not too large and your WAN links are fast, you may try this option before physically shipping the USB drive to the target location.
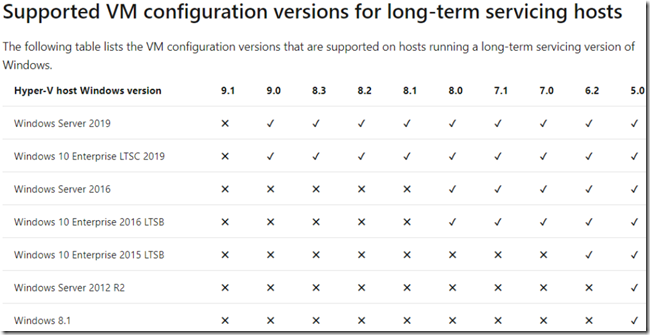
Supported Hyper-V Host and Guest Configurations
Below is a chart detailing which Windows operating system host versions support which Hyper-V guest versions. Make sure you are moving VMs between supported host and guest versions otherwise the process will fail.