In this post, we will set up a Windows Server 2012 and use RRAS to route IP traffic and to provide network address translation (NAT). The server will have two network interfaces and act as a router/firewall/NAT device. This type of configuration is useful if you plan to deploy a Sonicwall device in Layer2 bridge mode or transparent mode so that you can monitor network traffic in a non-disruptive manner. It is not recommended and definitely not best practice to have Windows Firewall alone be your front facing firewall. A firewall device is the best option to have as your edge device. Also note: You should not configure a Domain Controller as outlined below. Multihomed DC’s have nuerous issues. See article.
Note: This scenario is fantastic when combined with a non-intrusive, front facing firewall. Using the Windows firewall as the front facing firewall can be risky because adding programs or services will usually automatically open up a corresponding Windows firewall ports. If you forget to manually close those ports after a service or software install, you may be exposing your server. If however, you are not the forgetful type, Windows Server 2012 has an exceptionally good firewall and can do the job of a router/firewall/nat appliance.
The pre-requisites are as follow:
- Server 2012 installation with GUI
- Ethernet switch for LAN segment connection
- NIC 1 for public untrusted WAN network connection
- NIC 2 for private trusted LAN network connection
- The server should be a member server, NOT a DC.
To begin, let’s configure the LAN and WAN interfaces.
Open PowerShell, type ‘control panel’ and press enter. Select network and sharing center.
Click on change adapter settings. Right click on the Ethernet adapter that’s connected to your switch and select rename. Change its name to LAN.
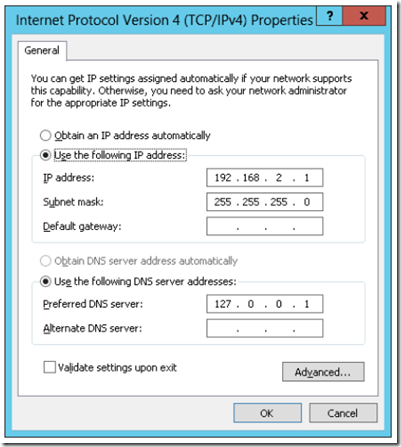
Now double click on the LAN adapter and select properties. Next, highlight TCP/IPV4 and change the configuration to the one shown below. Note: Do not enter a default gateway for the LAN. Only the WAN should have a default gateway. Make sure the LAN interface is connected to a switch.
You may need to consult with your ISP about the IP address, Subnet mask and Default Gateway but make sure that DNS is set to 127.0.0.1 since we are going to install the DNS server role.
Make sure that your WAN interface show up on the Public (untrusted) zone.
Next, click on the server manager icon on the bottom left hand side of the desktop. In the server manager, click on manage > add roles and features.
Select next to continue, then select role-based or feature-based installation. From the server list, select your server. Finally, add the server roles:
- DHCP Server
- DNS Server
- Remote Access
Click next until you reach Remote Access role services. Place a checkmark by DirectAccess and VPN as well as by Routing. Finish the installation.
Once again, click on server manager and select tools > routing & remote access from the server manager’s dashboard.
Right click on the server name and select configure and enable routing and remote access.
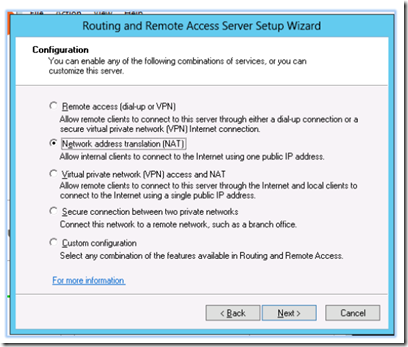
In the setup wizard, select network address translation (NAT)
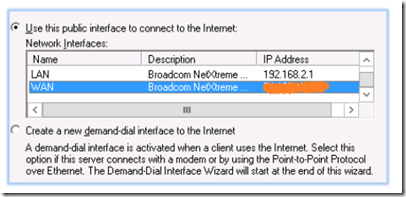
Select the WAN interface as the public interface.
If you get an error that states that you may not be able to connect due to firewall ports being closed, ignore it and continue.
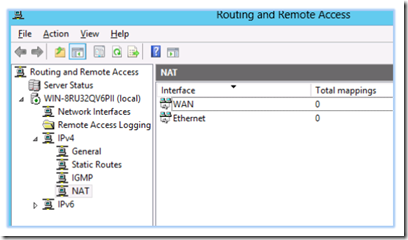
From the routing and remote access console, select IPV4 > NAT.
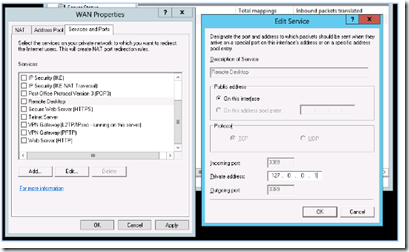
Double click on the WAN interface and select the services and ports tab. This is where you forward ports to your LAN subnet hosts.
The above image shows the opening of Remote Desktop port 3389 and subsequent forwarding to the server’s loopback address (127.0.0.1)
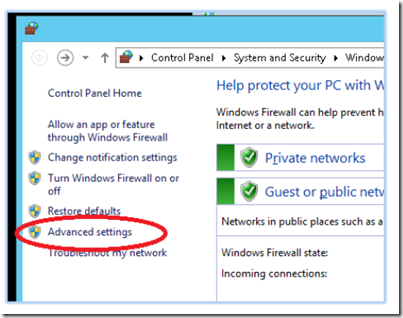
Open PowerShell and type firewall and press enter. Windows firewall console will display. Click Advanced Settings.
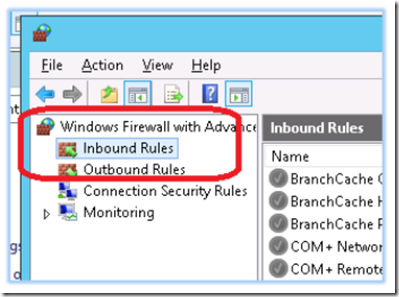
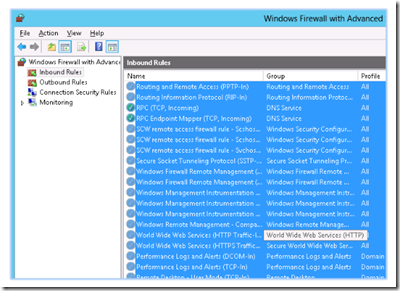
In Windows Firewall with Advanced Security, click on inbound rules.
Highlight all of the inbound rules, right click and select delete.
Doing this is the best way to avoid a mental lapse. Delete all the inbound rules and then add one at a time; as you need them.
To add an inbound rule, highlight inbound rule and select new rule from the actions pane.
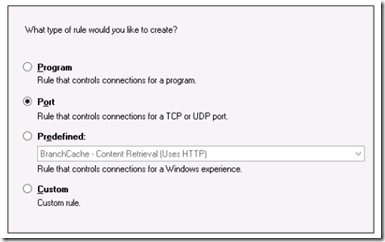
The new inbound rule wizard will appear. Follow these steps to add a rule for Remote Desktop:
Select a port to allow.
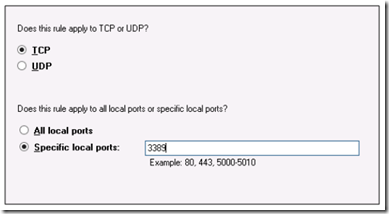
Select the protocol and port number.
Select allow the connection.
Select the zone where the firewall will allow traffic to traverse.
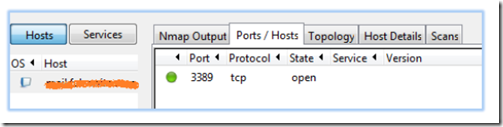
Give the rule a friendly name and click finish. After finishing, it’s a good idea to run NMap to make sure that only the specified ports are open.
The NMap image above confirms that only RDP-3389 is open.
Next set up the DHCP server (click here for instructions)
Once finished, connect a client PC to the LAN switch and voila! Your Windows 2012 server is now doing the job of a very capable firewall/router!